Search results
Search for "magnetic fluid" in Full Text gives 4 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
On the relaxation time of interacting superparamagnetic nanoparticles and implications for magnetic fluid hyperthermia
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1280–1289, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.127

- superparamagnetic regime in the presence of interparticle dipolar interactions is considered. The direct implications of such interactions for magnetic fluid hyperthermia therapy through susceptibility loss mechanisms give rise to an indirect method for their study via specific absorption rate measurements
- nanoparticulate contrasting agents on proton relaxivity [7][8][9]) and cancer therapy (through magnetic fluid hyperthermia therapy [10][11]). The efficiency of the magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in a colloidal system to convert the energy of AC magnetic fields into temperature increments is of high importance for
Magnetic-field sensor with self-reference characteristic based on a magnetic fluid and independent plasmonic dual resonances
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 247–255, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.23
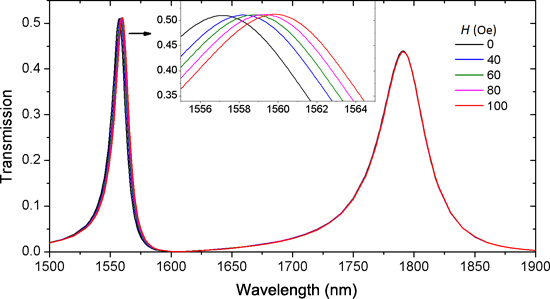
- , Tianjin 300222, China 10.3762/bjnano.10.23 Abstract A magnetic-field sensor with self-reference characteristic based on metal–dielectric–metal (MDM) plasmonic waveguides and a magnetic fluid (MF) is proposed and theoretically investigated. Independent dual resonances are supported by the coupled
- compactness of the MDM waveguide structure. This research may open new opportunities to design nanoscale magnetic sensors with good performance. Keywords: dual resonance; magnetic fluid; magnetic sensor; plasmonic waveguide; self-reference; surface plasmon polaritons; Introduction Sensors that can detect
- magnetic fluid. The background metal in the grey part is silver, the complex permittivity of which is characterized by the well-known Drude model: , where ε∞ = 3.7 is the permittivity at infinite angular frequency, the bulk plasma frequency is ωp = 1.38 × 1016 Hz, the damping frequency of the oscillations
Antitumor magnetic hyperthermia induced by RGD-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles, in an experimental model of colorectal liver metastases
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1532–1542, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.147

- hyperthermia values. SAR values above 900 W/g were obtained for the Fe3O4@PMAO_RGD MNPs dispersed in water at 14 kA/m and 606 kHz, where these NPs were selected as heating agents for in situ magnetic fluid hyperthermia protocols. The surgical model employed has proved useful to selectively deliver different
A facile method for the preparation of bifunctional Mn:ZnS/ZnS/Fe3O4 magnetic and fluorescent nanocrystals
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1743–1751, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.178

- applications. They can, for example, be used as a contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging or as therapeutic agents in magnetic fluid hyperthermia [9][10]. Several successful applications such as targeted drug delivery, bioseparation, biodetection, and labelling and sorting of cells [11][12][13][14] are






























